Table of Contents
How to Obtain License from DFTQC in Nepal
The Department of Food Technology and Quality Control (DFTQC) serves as Nepal’s primary food safety regulatory authority, ensuring that all food businesses meet stringent quality and safety standards. Obtaining a DFTQC license is mandatory for businesses involved in food production, processing, distribution, and service across Nepal. This comprehensive guide provides detailed information on how to obtain license from DFTQC in Nepal for three critical business categories: food manufacturing facilities, food importers, and restaurant/food service establishments.
Education Consultancy Registration in Nepal
Understanding DFTQC Licensing Framework
The DFTQC licensing system operates under Nepal’s regulatory framework, recently updated through the Food Hygiene and Quality Act, 2081 (2024), which supersedes the previous Food Act, 2023 (1967). This new legislation introduces enhanced compliance requirements and aligns Nepal’s food safety standards with international benchmarks. Food businesses must understand that DFTQC licensing is not merely a regulatory formality but a crucial component of ensuring public health and consumer safety.
Legal Foundation for DFTQC Licensing
The legal framework governing DFTQC licenses includes:
- Food Hygiene and Quality Act, 2081 (2024) – Primary legislation
- Food Act, 2023 (1967) – Foundational provisions
- Food Rules, 2027 (1970) – Operational procedures
- Nepal Food Standards – Technical specifications
- International Standards including Codex Alimentarius
DFTQC License Categories and Requirements
DFTQC categorizes food businesses into distinct license types based on operational scope and risk assessment. Understanding these categories is essential for successful license application and compliance.
| Business Type | License Category | Validity Period | Fee Range (NPR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Manufacturing | Category A | 3 years | 15,000 – 50,000 |
| Food Processing | Category B | 2 years | 10,000 – 30,000 |
| Food Trading | Category C | 1 year | 5,000 – 15,000 |
| Restaurant/Hotel | Category D | 1 year | 3,000 – 12,000 |
| Food Import/Export | Category E | 3 years | 25,000 – 75,000 |
Food Manufacturing License for Small Production Facilities
Food manufacturing licenses are essential for businesses engaged in producing food products, ranging from small-scale operations to large industrial facilities. Category A licenses specifically apply to food manufacturing operations and require comprehensive compliance with DFTQC standards.
Requirements for Food Manufacturing License
Small production facilities must meet specific infrastructure and operational requirements to qualify for DFTQC manufacturing licenses:
Infrastructure Requirements
- Production areas must maintain hygienic conditions consistently
- Segregation between raw and finished products is mandatory
- Pest control systems must be installed throughout facilities
- Quality control laboratory setup with appropriate testing equipment
- Storage facilities meeting prescribed requirements completely
Documentation Requirements
- Completed application form from DFTQC office
- Company registration certificate from relevant authorities
- Tax registration (PAN/VAT) certificates
- Municipal business license from local government
- Land ownership/lease documents with clear titles
- Building construction completion certificates
- Production process flowcharts with detailed specifications
- Quality control procedures manual
- HACCP (Hazard Analysis) implementation plan
- Laboratory testing protocols documentation
- Equipment specifications and calibration certificates
Step-by-Step Process for Food Manufacturing License
Phase 1: Business Classification Assessment
Food business categories are determined based on operations. Manufacturing scales get evaluated thoroughly. Risk assessment procedures are conducted systematically by DFTQC officials.
Phase 2: Infrastructure Development
Production facilities are established according to DFTQC standards. Quality control laboratories are set up properly. Storage facilities meet prescribed requirements completely.
Phase 3: Documentation Preparation
Application forms are filled out accurately. Supporting documents get compiled systematically. Technical specifications are prepared professionally.
Phase 4: Initial Inspection
DFTQC inspectors conduct preliminary facility visits. Infrastructure compliance gets verified thoroughly. Corrective measures are recommended when necessary.
Phase 5: License Issuance
Final approvals are granted after compliance verification. License certificates are issued officially. Operations can commence legally thereafter.
Quality Standards for Food Manufacturing
Food manufacturers must adhere to strict quality standards including:
- Product composition meeting specified standards for each category
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) implementation
- Good Hygiene Practices (GHP) compliance
- HACCP principles application where required
- Personnel hygiene standards maintained strictly
- Equipment cleaning procedures followed regularly
- Environmental monitoring systems operating continuously
Food Import License for Packaged Food Products
Food import licenses are mandatory for businesses bringing packaged food products into Nepal. Category E licenses specifically apply to food import/export operations and require specialized knowledge of international trade regulations and DFTQC import procedures.
Requirements for Food Import License
Importers of food products must meet specific regulatory requirements under the Food Hygiene and Quality Act, 2081:
Legal Requirements
- Obtain approval from DFTQC for importing food/food products
- Obtain entry permit from DFTQC before importing food items into Nepal
- Comply with quality standards specified by DFTQC
- Maintain proper documentation for all imported products
- Submit to inspection and testing as required
Documentation Requirements
- Import license application form from DFTQC
- Company registration certificate
- Tax registration (PAN/VAT) certificates
- Import/export registration certificate
- Product specifications and ingredient lists
- Certificate of analysis from manufacturer
- Label approval documentation
- Country of origin certificates
- Health certificates from exporting country
- Previous import records (if applicable)
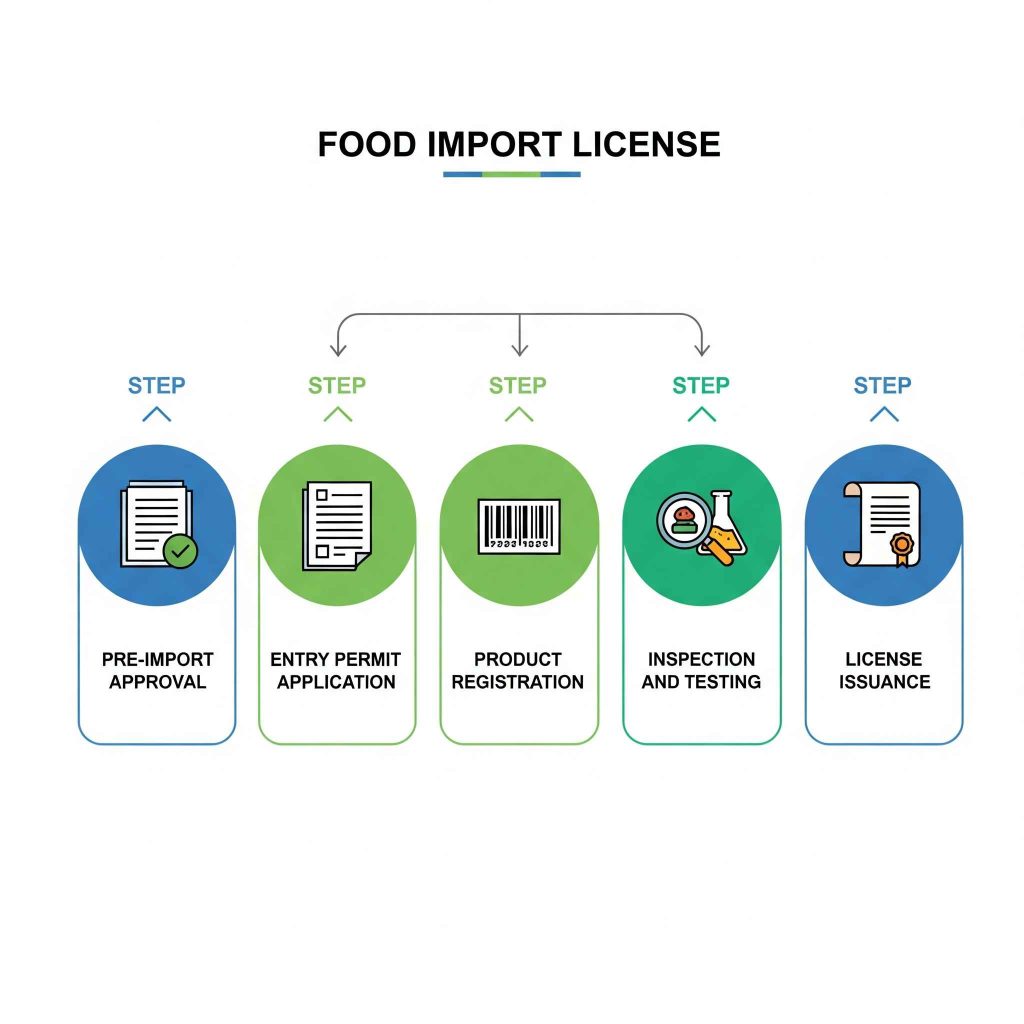
Step-by-Step Process for Food Import License
Step 1: Pre-Import Approval
Food business operators must obtain approval from DFTQC or designated office before importing food products. This involves submitting detailed product information and documentation for review.
Step 2: Entry Permit Application
Food products brought to entry points for importation must obtain entry permit from DFTQC or designated office before importing such items into Nepal. Non-compliance attracts penalty of NPR 50,000.
Step 3: Product Registration
Imported food products must be registered with DFTQC, including:
- Product composition details
- Label information in Nepali or English
- Nutritional information as required
- Shelf-life and storage conditions
- Manufacturer information and contact details
Step 4: Inspection and Testing
DFTQC officials may conduct inspection and testing of imported products to ensure compliance with Nepal food standards. Laboratory testing verifies product safety and quality.
Step 5: License Issuance
Upon successful completion of all requirements, DFTQC issues the import license valid for 3 years. Regular renewals are required to maintain compliance.
Labeling Requirements for Imported Food
Imported food products must comply with strict labeling requirements:
- Name of food and manufacturer’s name and address
- Weight or volume of item, selling price, batch number and date of production
- Expiry date and consumption period information
- Warning messages or symbols for potentially harmful products
- Nutritional information in specified format
- Language requirements – Nepali or English for imported products
Restaurant and Food Service Establishment License
Restaurant licenses and food service establishment licenses fall under Category D of the DFTQC licensing system. These licenses are essential for businesses serving food directly to consumers, including restaurants, hotels, cafes, and catering services.
Requirements for Restaurant License
Restaurant owners and food service operators must meet specific health and safety requirements:
Infrastructure Requirements
- Kitchen facilities must meet DFTQC hygiene standards
- Food storage areas must be properly maintained
- Hand washing facilities must be available and functional
- Waste disposal systems must be adequate and sanitary
- Ventilation systems must ensure proper air circulation
- Pest control measures must be implemented
Documentation Requirements
- Restaurant license application form
- Business registration certificate
- Tax registration (PAN/VAT) certificates
- Municipal business license
- Land ownership/lease documents
- Building completion certificate
- Menu and food items list
- Food supplier information and contracts
- Staff health certificates
- Food safety management plan
Step-by-Step Process for Restaurant License
Step 1: Business Registration
Restaurant businesses must first register with appropriate authorities:
- Company registration with Company Registrar’s Office
- Tax registration with Inland Revenue Department
- Municipal business license from local government
Step 2: Infrastructure Preparation
Restaurant facilities must be prepared according to DFTQC standards:
- Kitchen layout must ensure proper workflow
- Food storage areas must be separate and appropriate
- Dining areas must meet hygiene requirements
- Washroom facilities must be adequate and clean
Step 3: Documentation Submission
Complete documentation must be submitted to DFTQC:
- Application form with all required information
- Supporting documents as listed above
- Food safety management plan
- Staff training records
Step 4: Inspection Process
DFTQC inspectors conduct thorough inspection of restaurant premises:
- Kitchen facilities and equipment inspection
- Food storage and handling practices review
- Staff hygiene practices assessment
- Overall cleanliness and maintenance evaluation
Step 5: License Issuance
Restaurant license is issued upon successful inspection and compliance verification. Category D licenses are valid for 1 year and require annual renewal.
Food Safety Requirements for Restaurants
Restaurant operators must implement comprehensive food safety measures:
- Temperature control for food storage and service
- Cross-contamination prevention procedures
- Allergen management systems
- Staff hygiene protocols
- Cleaning and sanitization schedules
- Pest control programs
- Food recall procedures if needed
DFTQC License Processing Timeline and Fees
Understanding the timeline and fee structure is crucial for successful DFTQC license application. The process typically takes 32 days from application to license issuance.
Processing Timeline
| Application Stage | Duration | Authority | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application Review | 7 days | DFTQC Office | Document verification |
| Technical Evaluation | 10 days | Technical Team | Standard compliance check |
| Site Inspection | 5 days | Inspector Team | Facility assessment |
| Compliance Review | 7 days | Quality Section | Final evaluation |
| License Issuance | 3 days | Director General | Certificate preparation |
| Total Timeline | 32 days | Complete Process | Full Approval |
Fee Structure
DFTQC license fees vary based on business category and operation scale:
Food Manufacturing License Fees
- Category A (Food Manufacturing): NPR 15,000 – 50,000
- Validity: 3 years
- Additional costs: Laboratory testing, inspection fees
Food Import License Fees
- Category E (Food Import/Export): NPR 25,000 – 75,000
- Validity: 3 years
- Additional costs: Product testing, documentation fees
Restaurant License Fees
- Category D (Restaurant/Hotel): NPR 3,000 – 12,000
- Validity: 1 year
- Additional costs: Inspection fees, renewal charges
Common Challenges and Solutions
Businesses often face challenges during the DFTQC licensing process. Understanding these challenges and their solutions can help ensure successful application.
Documentation Challenges
Incomplete documentation is the most common reason for application delays. Solution: Prepare all required documents systematically and seek professional guidance if needed.
Infrastructure Compliance
Facilities that don’t meet DFTQC standards can cause application rejection. Solution: Conduct pre-inspection assessment and make necessary improvements before application.
Timeline Delays
Processing delays can occur due to high application volume or incomplete submissions. Solution: Submit complete applications well in advance of planned operations.
Regulatory Changes
Frequent regulatory updates can create compliance challenges. Solution: Stay informed about legal developments and maintain regular communication with DFTQC officials.
Provincial DFTQC Office Locations
DFTQC has offices across Nepal’s provinces to facilitate license applications and compliance monitoring:
| Province | Office Location | Contact Information | Jurisdiction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bagmati | Kathmandu (Babarmahal) | 01-4262369 | Central Region |
| Gandaki | Pokhara | 061-460448 | Western Region |
| Lumbini | Butwal | 071-540022 | Mid-Western |
| Karnali | Surkhet | 083-520156 | Far-Western |
| Sudurpashchim | Dhangadhi | 091-521847 | Far-Western |
License Renewal and Amendment Process
DFTQC licenses require regular renewal and may need amendments for business changes.
Renewal Requirements
- Applications must be submitted before expiry dates
- Updated documentation becomes necessary for renewals
- Facility inspections are conducted periodically
- Renewal fees must be paid as per current rates
Amendment Procedures
- Business expansion requires license amendments
- Product line additions need formal approvals
- Facility relocations demand fresh applications
- Ownership changes require license updates
FAQ Section: Common Questions About DFTQC Licensing
For Food Manufacturing Businesses
What is the minimum infrastructure required for food manufacturing license?
Food manufacturing facilities must have dedicated production areas, quality control laboratory, proper storage facilities, pest control systems, and adequate waste disposal mechanisms. Infrastructure requirements vary based on product type and scale of operation.
Where is the DFTQC office located for food manufacturing license applications?
DFTQC has offices in all provinces, with the main office at Babarmahal, Kathmandu. Applications can be submitted to provincial offices based on business location.
What are the common reasons for food manufacturing license rejection?
Common rejection reasons include inadequate infrastructure, incomplete documentation, non-compliance with hygiene standards, and failure to meet quality control requirements
For Food Importers
What is the process for obtaining entry permit for imported food products?
Entry permits must be obtained from DFTQC before importing food products. Process includes product registration, documentation submission, inspection, and approval. Non-compliance can result in NPR 50,000 penalty.
Where is the inspection conducted for imported food products?
Inspections are conducted at designated entry points by DFTQC officials. Products may be tested for compliance with Nepal food standards before clearance.
What are the labeling requirements for imported packaged food?
Imported food must have labels in Nepali or English including product name, manufacturer details, weight/volume, production date, expiry date, nutritional information, and warning messages where applicable.
For Restaurant Owners
What is the validity period for restaurant license in Nepal?
Restaurant licenses (Category D) are valid for 1 year from issuance date and require annual renewal with updated documentation and inspection.
Where can restaurant owners get training on food safety standards?
DFTQC provides training programs on food safety standards. Restaurant owners can also consult with food safety consultants for specialized training and guidance.
What are the key hygiene requirements for restaurant kitchens?
Restaurant kitchens must maintain proper temperature control, prevent cross-contamination, ensure staff hygiene, implement cleaning schedules, and maintain adequate waste disposal systems.
Conclusion: Your Path to DFTQC License Success
Obtaining a DFTQC license in Nepal requires careful planning, thorough preparation, and strict compliance with regulatory requirements. Whether you’re establishing a food manufacturing facility, importing packaged food products, or operating a restaurant, understanding the specific requirements for your business category is essential for success.
The Food Hygiene and Quality Act, 2081 (2024) has introduced enhanced compliance standards that align Nepal’s food safety regulations with international benchmarks. Businesses that embrace these standards not only achieve legal compliance but also build consumer trust and enhance their market competitiveness.
Call to Action for Each Target Audience
For Small Business Owners Starting Food Manufacturing
Begin your food manufacturing journey by conducting thorough infrastructure assessment and documentation preparation. Consult with DFTQC officials or food safety consultants to ensure your facility meets all requirements before submitting your Category A license application.
For Food Importers
Streamline your import operations by establishing strong relationships with DFTQC offices and maintaining comprehensive product documentation. Stay updated on regulatory changes and ensure all imported products meet Nepal food standards to avoid delays and penalties.
For Restaurant Owners
Transform your restaurant business by implementing robust food safety systems and maintaining excellent hygiene standards. Regular staff training and continuous compliance monitoring will ensure your Category D license remains valid and your business thrives.
Remember: DFTQC licensing is not just about regulatory compliance—it’s about ensuring the safety and quality of food for all Nepalese consumers. Invest in proper licensing today to build a successful and sustainable food business in Nepal’s growing market.
Corporate Biz Legal & Company Darta Nepal is a trusted law firm in Nepal, providing expert company registration services in Nepal with full legal compliance and professional support.




